| Tuesday | Thursday | ||||
|
1-18-05
Introduction to "Visual Math" |
The Pythagorean Theorem 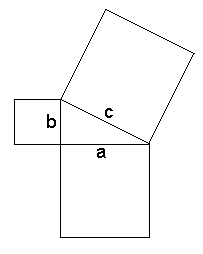 a2 + b2 = c2 |
||||
| 1-25 The Pythagorean Theorem (finished!)  |
|
||||
| 2-1-05 Regular and Semi- regular Tilings of the Plane 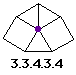
|
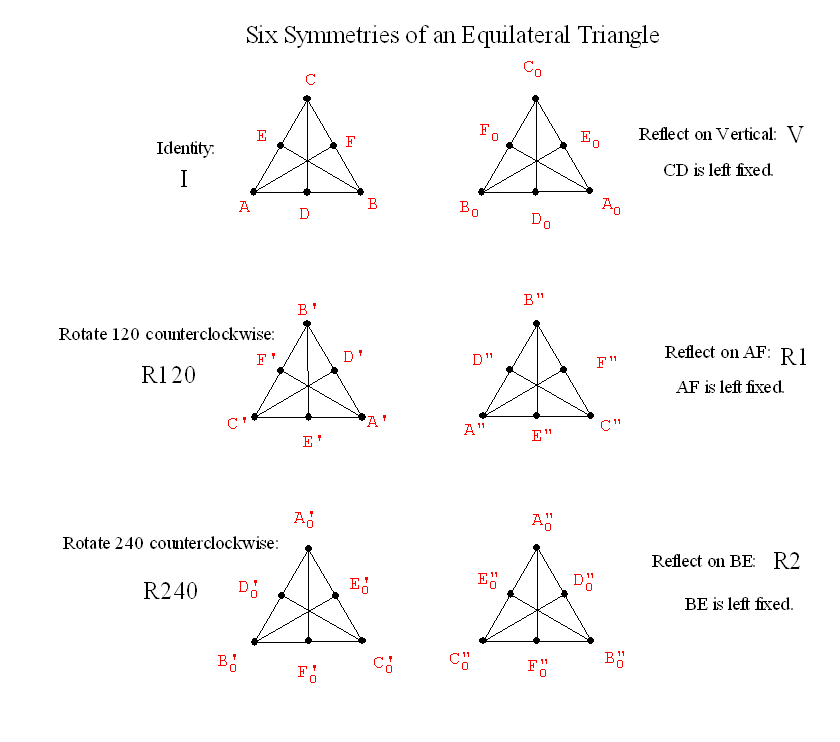
2-3-05 Finish Semi-Regular Tilings Symmetries for a Single Polygon Reflections and Rotations 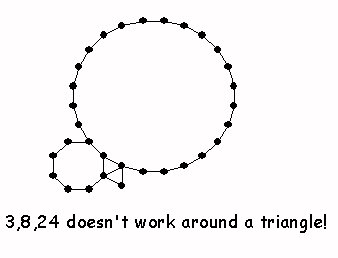 |
||||
 |
2-10
Symmetries for a Tiling of a Frieze and the Plane ...|p|q|p|q|p|q|p|q|p|q|p|... ...|d|b|d|b|d|b|d|b|d|b|d|... 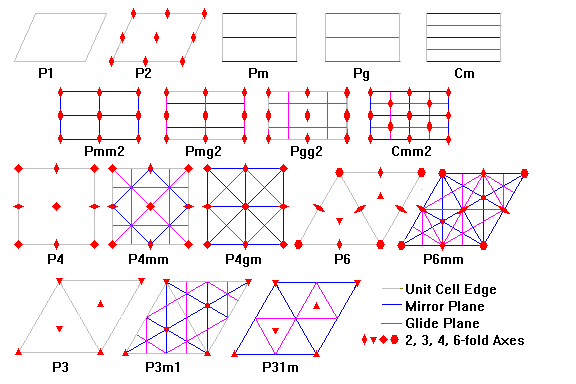
|
||||
| 2-15 Lab: WinGeometry and Surfing  |
2-17 Isometries in Symmetry Groups and planar tilings. Begin Space- Symmetries and Isometries Rotations and Reflections 
|
||||
| 2-22 Isometries Begin Space- How do we encounter space? |
2-24 Finish Classification of Isometries in the Plane Spatial Objects- How do we understand them? |
||||
| 3-2 Spatial Objects: Getting Familiar with The Platonic Solids. Counting in geometry and topology. What are topological properties?
|
V+R = E + 2
|
||||
| 3-8 Appplications of the Euler Formula "A Hard Problem" What's possible and what's impossible! The Utilities Problem and Complete Graphs in the Plane! 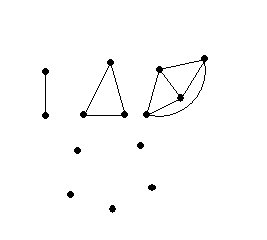 |
3-8
Appplications of the Euler Formula The Color Problems on the plane and the sphere and ... Creating a Klein Bottle 
|
||||
| 3-22 Maps and Coordinates for Surfaces Flatland, The Earth and The Torus.
|
|||||
|
3-29
More on Surfaces Adventures on the Mobius Band, the Klein Bottle, and the Projective Plane ! "New" Surfaces and The Classification of Surfaces
|
3-31 No Class Cesar Chavez Day |
||||
|
4-5 (Finish 3-29) "New" Surfaces and The Classification of Surfaces 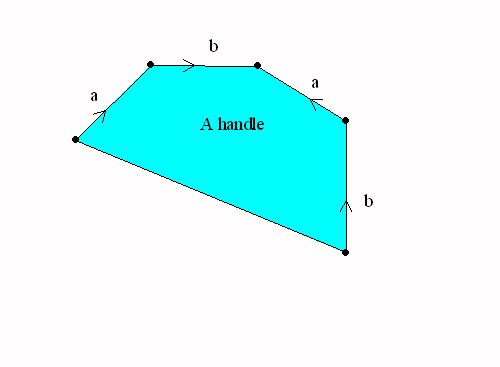 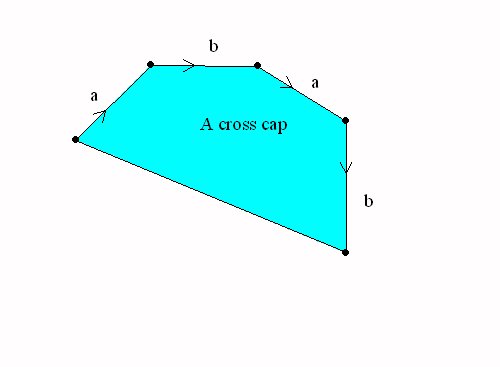 |
4-7 Similarity in the plane and space. Geometric Sequences and Geometric Series
|
||||
| 4-12 Space Filling Curves
|
4-14 Projective Geometry: Cones and Conic Sections Preliminaries for "Calculus" 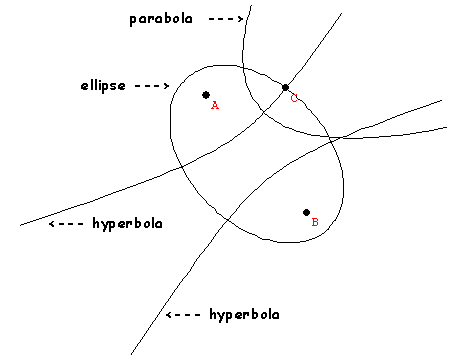 |
||||
| 4-19 Ch. 10.1 Some Historical Problems of Visualization: The parabola and squares. Visualizing Algebra, Motion and Change Analytic geometry- Descartes and Fermat 10.2 Four Problems Connecting the visual to the Numerical Motion and distance travelled; Motion and position; Tangent line; Area of a region. |
4-21 10.2 Four Problems Connecting the visual to the Numerical Motion and distance travelled; Motion and position; Tangent line; Area of a region. 10.3, 10.4:Newton: Tangent lines, velocity, and the derivative. 10.5, 10.6 Determining position and areas. |
||||
| 4-26
Calculus: Putting concepts together with computations. 10.7 See notes from 4-21 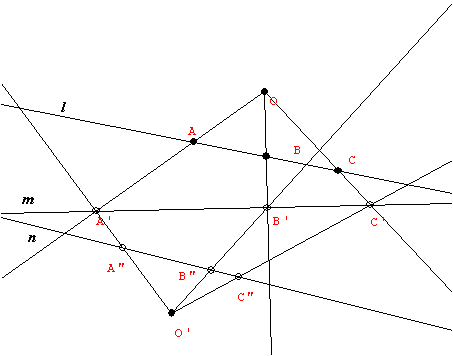 Projective Geometry: Desargues' Theorem and The Conics! |
4-28 An Introduction to Desargues' Theorem 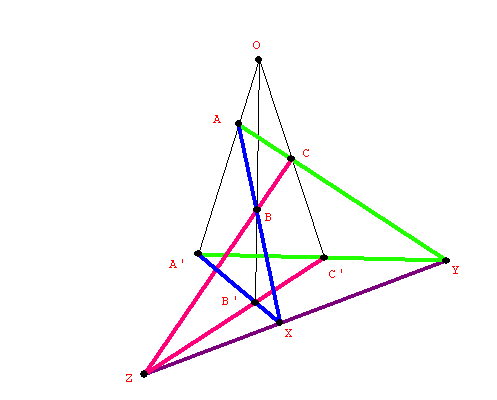 Perspective and Projective Geometry |
||||
5-3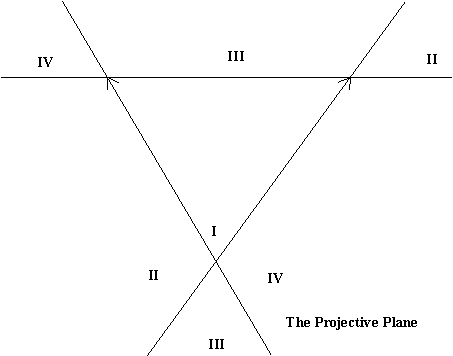 Perspective in Space and The Projective Plane |
5-5 Other Worlds and Surfaces: A Non-euclidean Universe5-5 |
||||
| Inventory References are to Notes from Spring 2004 |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|
2-26 The Platonic and Archimedean Solids.
|
||||
3-2 More on Solids. Symmetry. Isometries in Space.
|
3-4 Connections between Polyhedra. Frameworks. Duality. Similarity in the plane and space.  |
||||
3-9 More on Similarity, Geometric Sequences, and Series |
3-11 Space Filling Curves
|
||||
3-23 Encounters with The Fourth Dimension The Hypercube. 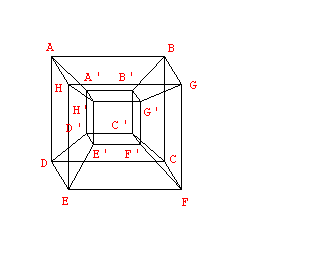  |
3-25 More on the Hypercube:Coordinates  |
||||
Coordinates for the Hypercube and the Tower of Hanoi                *
* * *                 |
|||||
| |
|||||
|
4-15 More on Surfaces  |
||||
|
4-22
The Classification of Surfaces Euler's Characteristic Number "New" Surfaces Cones and Conic Sections- Projective Geometry  |
||||
| 4-27 More on the Conics Projective Geometry: An Introduction to Desargues' Theorem  |
4-29 Perspective and Projective Geometry Perspective in Space and The Projective Plane  |
||||
| 5-4 More about Perspective and the Projective Plane  |
5-6 Other Worlds and Surfaces: A Non-euclidean Universe. 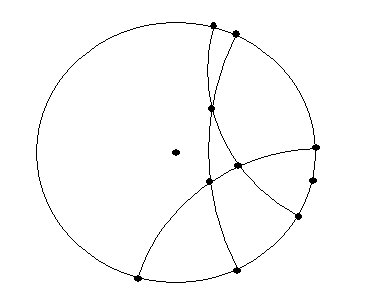
|
||||
|
Maps and Projective Geometry
|
||||
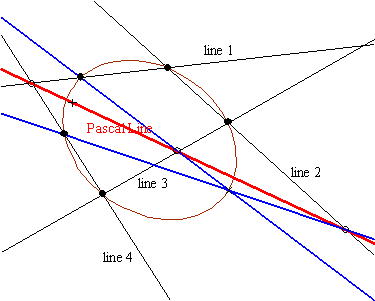
Projective Geometry: Desargues' Theorem ,Duality, Pascal's Theorem and The Conics! 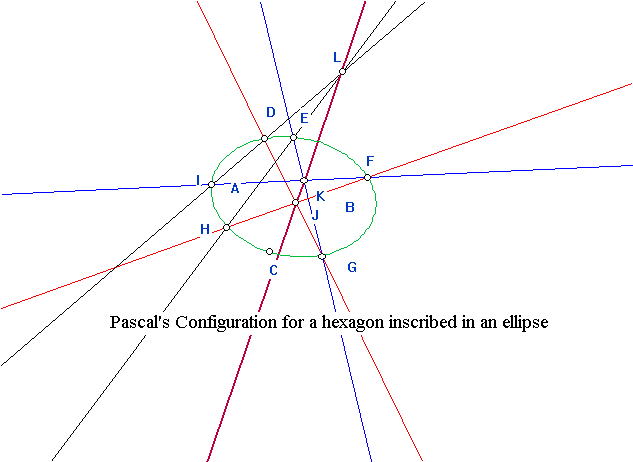 |
|||||
| Some Historical Problems of Visualization: Ch. 10.1 The parabola and squares. visualizing algebra Motion and Change visualized Analytic geometry- Descartes and Fermat |
Four Problems Connecting the visual to the Numerical10.2 Motion and distance travelled Motion and position. Tangent line Area of a region. |
||||
| Newton: Tangent lines, velocity, and the derivative. 10.3, 10.4 |
Determining position and areas. 10.5, 10.6 |
||||
| Putting concepts together with computations. 10.7 |
Dissection
Theorem for Regular Polygons |
||||