Last class we started a discussion of
Surfaces:Mark Sudduth's web page of surfaces.[ A physics master's degree student at UT, Arlington.
What is a surface?
Bounded, unbounded:
Closed, open:
With or without boundary:
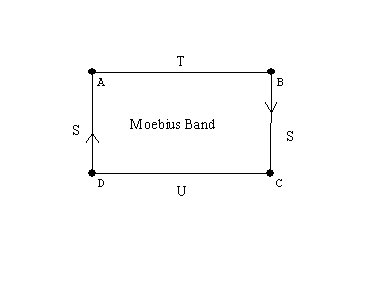
Orientable or Non-orientable: we considered the moebius band and the Klein Bottle as examples of non-orientable surfaces.
Can be realized (imbedded) in a plane, in 3 space, in 4 space.
Can be visualized (immersed) in ...
Examples:A closed disc, an open disc, a
plane, an annulus- cylinder, a mobius band;

Experiments with the mobius band. Drawing a curve along the center of the band we cover both "sides." Cutting along that curve the band does not fall apart, but gets twice as long!
a sphere,
a torus
a Klein bottle
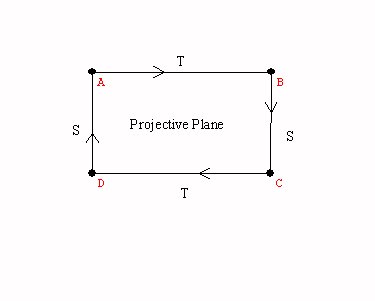
the projective plane... Why is this a closed and bounded surface?
Activity:Graphs on the torus.
Games and puzzles on the torus and the klein bottle.
From the Fun Fact files,
hosted by the
Harvey Mudd College Math Department , Unbelievable Unlinking
Imagine that the two objects in Figure 1 are solid (with thickness) and made of very flexible and stretchy rubber. Question: is it possible to deform one object into the other in a continuous motion (without tearing or cutting)? Surprise answer: Yes!! Hint: it is important that the object is solid and has thickness; this transformation cannot be done with a one-dimensional piece of string. It is also not possible to do this with a piece of rope because even though the rope has thickness, it is not flexible or "stretchy" enough. See below for an explanation and animated gif. Or, don't scroll down if you want to think about it a while! The Math Behind the Fact: Graeme McRae has generously contributed the
animated gif in Figure 2, showing another solution to
this problem! (Thank you, Graeme!) |
Visualizations of surfaces by flattened
- cut apart models.
A cylinder, a mobius band, the torus, the Klein bottle, the projective plane.
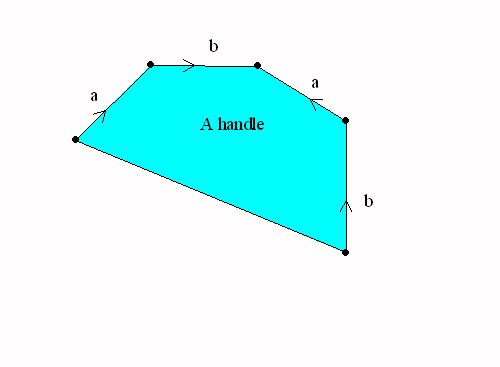
Closed Surfaces: Handles and cross-caps attached to the sphere.
|
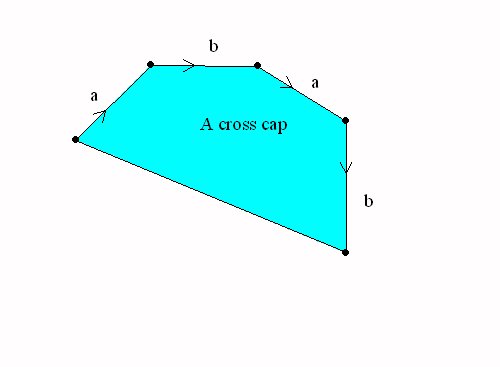
|

A sphere with a handle = a torus |

A Sphere with a cross cap = the projective plane |
The Topological Classification of "closed surfaces."
Every connected closed and bounded surface is topologically equivalent to a sphere with handles and crosscaps attached.