An isometry is a transformation that preserves the distance between
points.
reflections, rotations, translations, and glide reflections.
The Product of isometries:
The product of two reflections is either a rotation (if the axes of the reflection intersect) or a translation (if the axes of the reflection are parallel).
We have discussed four isometries:
reflections, rotations, translations, and glide reflections.
The Product of isometries:
The product of two reflections is either a rotation (if the axes of the reflection intersect) or a translation (if the axes of the reflection are parallel).
Wingeometry demonstration for reflection- one and two reflections
Any plane isometry is
either a reflection
or the product of two or three reflections.
What about 3 reflections?
Three reflections = reflection or glide reflection
Visual Proof discussion from Math 371 (HSU Geometry Course):
Key idea- The product of two reflections is "flexible."
discuss
basic idea:
Reflection is related to "perpendicular bisector" of PP'
With a triangle the 3 vertices ABC -> A'B'C' may be related to at
most
3 lines of reflection.
Proof: Click here!
What about 3 reflections?
Three reflections = reflection or glide reflection
Visual Proof discussion from Math 371 (HSU Geometry Course):
Key idea- The product of two reflections is "flexible."
Space:
How do we understand objects in space?
How can the Flatlander experience the sphere and space?
Pick up templates to make Platonic solid models for next class!
The simplest three dimensional figure has 4 points not all in the same plane: three point determine a plane- so a fourth point not in that plane will need "space" to make sense. These four points determine a tetrahedron.
Cross sections: Look at the tetrahedron with cross sections : Triangles, what if the tetrahedron starts through Flatland with an edge first?
Pick up templates to make Platonic solid models for next class!
The simplest three dimensional figure has 4 points not all in the same plane: three point determine a plane- so a fourth point not in that plane will need "space" to make sense. These four points determine a tetrahedron.
Cross sections: Look at the tetrahedron with cross sections : Triangles, what if the tetrahedron starts through Flatland with an edge first?
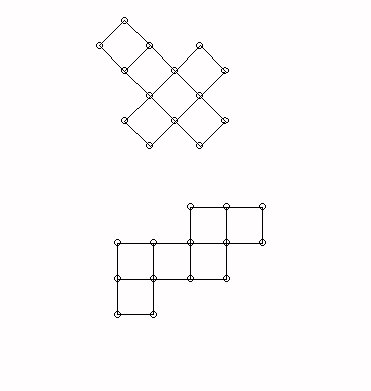
Fold downs- flattened figures: Consider how the cube can be assembled from folded down squares in two different configurations: a cross or a "zig-zag."