Due
1. a. A real valued function of two variables, f : R2->R is called homogeneous of degree m if for any real numbers x,y,and t,
b. Generalize your result to homogeneous differentiable functions of 3 and 4 variables.
2. The temperature distribution on a metal plate at time t is given by the function H t of x and y:
a) Describe the motion of the particle if it is located at (0,0) when t=0 and adjustments are made when t = 0,1,2,3,4,... etc.
b) Describe the motion of the particle if it is located at (0,0) when t=0 and adjustments are made when t = 0,1/2,1,3/2,2,... etc.
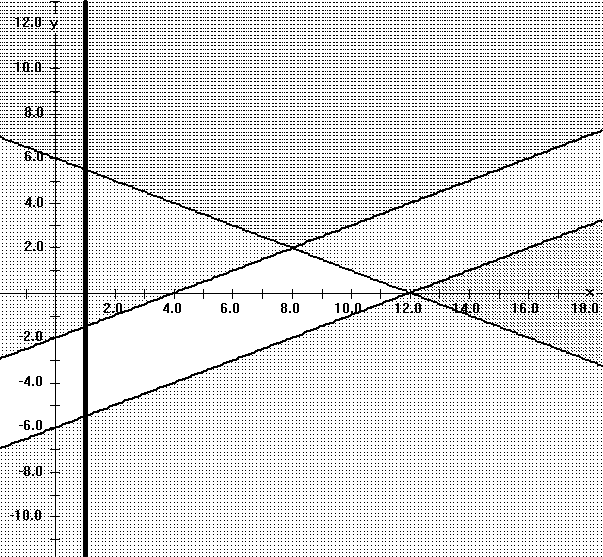
Suppose T is a triangular region in the plane.
Suppose L(x,y) = Ax + By where A and B are constants that are not both 0.
Use the LaGrange theory to explain why the maximum (or minimum ) values of L for the region T will occur at one of the vertices of the triangle.
State and justify the analogous result for planar regions
bounded by quadrilaterals and pentagons.
Apply this work to find the maximum and minimum values of L(x,y)
=
3x + 5y when (x,y) satisfy all the following (linear)
inequalities:
12 > = x + 2 y;
4 < = x- 2y ;
and 1 < = x.
3 Bonus Points: Generalize this problem to one of the
following situations:
a. A
tetrahedron in space with L(x, y, z) = Ax
+ By + Cz with A,B, and C not all 0.
b. A planar
region bounded by a polygon with n sides.
Justify your statement and illustrate it with an example.